Corpus-based Analysis [1]


Corpus Annotation is NOT the must
Corpus Annotation is the need when no choice.
empirically.empiricismepiphenomena - output on the large scale, or either the blood-flow requirements or some other psysiological feature associated with it.Distribution : toward Unified Empirical Linguistics [1], where evidence of all kinds - textual, psychological and neurological - is a matter of course used in concert to uncover the nature of language. In such context, corpus linguistics will reach its full potential as a
methodology.
A corpus does not contain new information about language, but the software offers us a new perspective on the familiar.
- Two related processes: the production of frequency lists (either in rank order, sorted alphabetically, or according to keyness) and the generation of concordances (examples of particular items in context) -> Note Bene.: In order to compare frequency counts across corpora of different sizes, a process of normalisation is required.
Now, what can concordance/frequency reveal the unknown?

Only 4 lines (lines 5, 13–15) is now clause-medial, and acting as a temporal adverb ; with remaining clause-initial and has discourse-level functions, signalling a change of focus or topic !!!
the black experience (taken from Obama’s speech from a 450-million-word Bank of English corpus.)
the + group of people + experience !!Patterns can also be interpreted as a co-occurrence of a language form and a particular context.
collocation system demo Just-the-word
[1] Write an essay: How to use corpus (linguistics) to (write dictionaries | the study of health communication | language teaching and learning | ........)
[2] Annotate a text with (word sense | pos | polarity| discourse marker | named entity | ......)
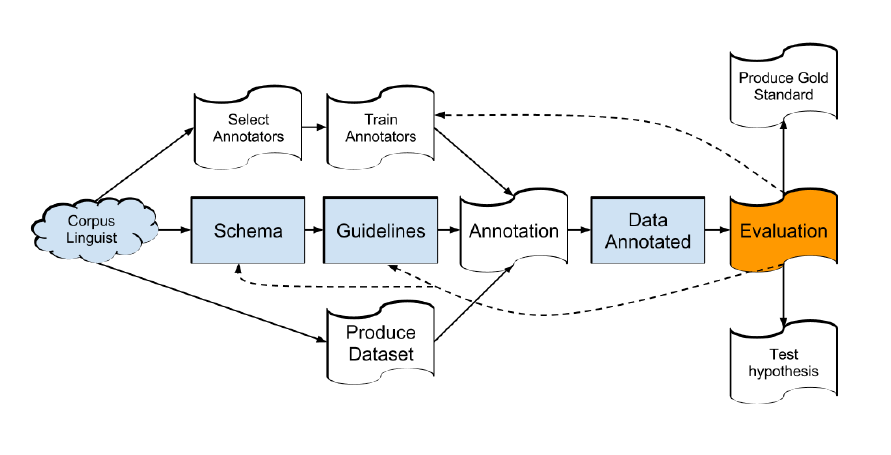
(Prevor, 2014)
Annotation Schema: explicit characterization of the units/categories/...that will need to be annotated, and markup language as well (e.g., XML).
Annotation Guidelines:

Shower Presentation Template
Author: Vadim Makeev, Opera Software
Modified: Ramnath Vaidyanthan, for Slidify